Sound Adjustment Mode
About Sound Adjustment Mode
The system has several features that allow you to adjust the acoustic characteristics inside the cabin.
| Item | Function | Page |
|---|---|---|
| Parametric EQ | You can adjust the 7-band parametric equalizer.This mode is also used to automatically measure the frequency characteristics in the vehicle, and automatically adjust to the smooth characteristics with low distortion based on the measurement data. | Parametric equalizer adjustment (PEQ) |
| Time Alignment | The delay time and level for the sound from each speaker
can be adjusted in order to correct any phase mismatches in the sound
resulting from the listening position.This mode is also used to automatically measure and adjust
the sound arrival time in the vehicle. * The Time Alignment cannot be specified together with Position selector. | Time alignment adjustment (Time Alignment) |
| Position selector | You can select the speaker level
or balance that was preset in each seat. * This mode cannot be specified together with Time Alignment. | Position selector |
| Cross over | Specified frequency bands are allocated to each speaker for improved sound integration. | Crossover adjustment (X-Over) |
| Multi-harmonizer | When original sounds are converted to MP3/WMA format, frequency ranges that are not normally audible to the human ear are compressed. The multi-harmonizer can be used to play back these compressed sounds at as close to their original from as possible so that clear and powerful sound can be enjoyed. | Multi-harmonizer settings (Harmonizer) |
| Non-fader setting | The sub-woofer settings can be performed. | Non-fader settings (Non-F Setting) |
About parametric EQ
Various materials such as sheets or glass are used in the vehicle, absorbing or reflecting sound in different directions. The parametric EQ adjusts and corrects the peak and dip of the frequency.

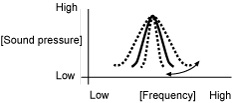
An "equalizer" is a function that corrects these peaks and dips in order to flatten the frequency characteristics. However with a normal graphic equalizer, the median frequency and the Q (sharpness and band width) are fixed, so that when neighboring bands are corrected, there is a limit to the amount by which distortion in the peak and dip characteristics can be corrected. A "parametric equalizer" lets you adjust the median frequency, Q (sharpness and band width) and gain to variable levels, so that you can make fine adjustments to spot areas of the frequency band.
[Parametric equalizer characteristics]
1. Median frequency can be varied.

2. Gain can be varied.

3. Q (sharpness/band width) can be varied.
About time alignment
With vehicle audio systems, the installation position of the speakers and the position of the listener mean that the distances from the listener to the left and right speakers are almost always different. These differences in the distance from the listener to each speaker in turn means that the time taken for the sound to reach the listener is different for each speaker. The result of this is that the phases of each speaker (biases) become mismatched and the sound becomes unnatural, as though the sound stage is not wide enough. The “time alignment" function corrects the time taken for the sound waves to reach the listener in order to set the optimum phase for the listening position so that the sound becomes more expansive as though it is being listened to on a sound stage.
The basic adjustment method involves measuring the actual distances to each speaker and calculating the differences in distance relative to the most distant speaker in order to derive the delay time for the sound from each speaker.

About crossover
The frequency band that is stored by audio media such as CDs is a fairly wide range from 20 Hz to 20 kHz, and it is difficult for a single speaker to be able to play back all frequencies in such a wide range.
Because of this, several speakers can be used, with different frequency bands (such as treble, medium and bass) allotted to each speaker so that wide frequency ranges can be played back. The "Crossover" function is used to allot the frequency ranges that are to be played back by each speaker in accordance to the installed speaker units and the layout of the speakers, in order to obtain the maximum level of performance from the speakers and to provide the most stable frequency characteristics.
The crossover function includes a high-pass filter (HPF) for playing back treble sounds, and a low-pass filter (LPF) for playing back bass sounds. In addition, the HPF and LPF are used in combination in order to play back sounds in the mid range.

For example, when adjusting the HPF, frequencies that are lower than the specified frequency are progressively dampened, rather than simply not being played back at all. The "slope" adjustment function is the function that is used to adjust these dampening characteristics.
The slope characteristics of a filter are such that with larger slope values (for example 12 dB/oct), the slope becomes steeper, and so the amount of sound mixing in with neighboring bands becomes less so that only the target band is played back. However, it also causes the merging of sound between speakers to become poorer and can result in greater distortion.
The crossover function is a filter that allocates the specified frequency bands.
A high-pass filter (HPF) is a filter that cuts out frequencies that are lower than the specified frequency (bass range) and allows higher frequencies (treble range) to pass through.
A low-pass filter (LPF) is a filter that cuts out frequencies that are higher than the specified frequency (treble range) and allows lower frequencies (bass range) to pass through.
The slope is the signal level at which frequencies that are one octave higher or one octave lower are dampened.
This system supports the basic speaker systems which comprise front speakers, rear speakers and an added sub-woofer if necessary. In such cases, the crossover can be used to apply the HPF to the front and rear speakers and the LPF to the sub-woofer so that the sound from all speakers merges properly.