Glossary
Please read the descriptions for following terms to enjoy more.
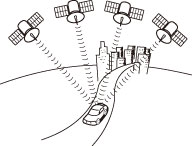 | GPS is a system to detect current location (latitude, longitude, altitude) by receiving radiowaves from normally 4 or more, or 3 in some cases, GPS satellites orbiting 21,000 km over the Earth. These satellites are launched and managed by the US Department of Defense mainly for military use, but are also open for private usage. This unit performs navigation using the GPS information, various sensors, and road map data. |
| Wide area map is a map with wide area, and detailed map is a map of small area. The scales of a map are 1/20,480,000, 1/10,200,000, 1/5,120,000, 1/2,560,000, 1/1,280,000, 1/640,000, 1/320,000, 1/160,000, 1/80,000, 1/40,000, 1/20,000, 1/10,000, and 1/5,000. |
 | GPS position quality is displayed at left lower.The more bars light, the more extreme precision GPS position quality is. |
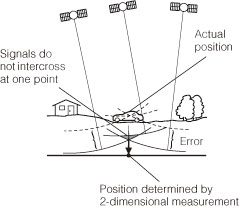 | GPS calculates the position using the triangulation. Distance to the satellite can be determined when the radiowave from that satellite is received, and current location can be measured by receiving radiowave from 3 satellites. However, since there are margin of error in the GPS satellites and navigation unit, only 2 dimensional measurement of latitude and longitude is performed when radiowave from only 3 satellites are received. The precision will be lower in this case. The measurement will be taken in 3 dimensions of latitude, longitude, and altitude when radiowave from 4 or more GPS satellites are received. 3 dimensional measurement has higher precision than 2 dimensional measurement, and error of vehicle location becomes smaller. |